| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
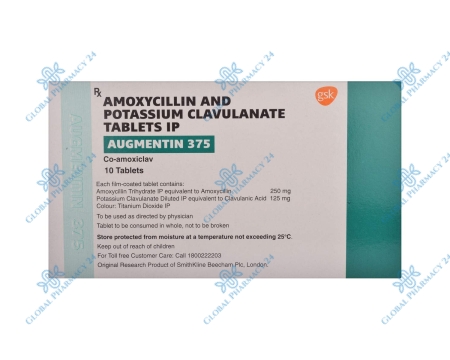
| Active Ingredients | Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium |
| Formulations | Oral tablets, Chewable tablets, Liquid suspension |
| Indications | Bacterial infections including respiratory, urinary tract, skin, and sinus infections |
| Dosage Forms | 250mg/125mg, 500mg/125mg, 875mg/125mg |
| Duration of Treatment | Typically 7-14 days depending on the infection type |
| Side Effects | Nausea, diarrhea, rash, and possible allergic reactions |
| Global Availability | Widely available in pharmacies across the USA and worldwide |
An Overview of Augmentin
Augmentin is a leading antibiotic medication, combining amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium to offer a broad-spectrum solution against bacterial infections. Its efficacy is rooted in its ability to fight against a wide range of bacteria, making it a preferred choice for healthcare providers in treating various infections. The combination of these two active ingredients enhances the drug's ability to overcome bacterial resistance, a common issue with many antibiotics.
This pharmaceutical product has been instrumental in managing infections by providing a potent solution that addresses both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Its formulation is designed to target the cell wall synthesis of bacteria, which is crucial for their survival. By doing so, Augmentin effectively halts the spread of infections, ensuring a comprehensive approach to bacterial eradication.
Augmentin – A Powerful Combination Drug
Augmentin stands out in the pharmaceutical market as a combination drug that leverages the synergistic effects of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium. This blend not only broadens the spectrum of bacterial targets but also counters potential resistance, making Augmentin a formidable opponent against challenging infections.
Manufacturing and Global Availability of Augmentin
The production of Augmentin is upheld by stringent quality control measures to ensure its safety and effectiveness. Available globally, it caters to the needs of patients across different regions, facilitated by a robust distribution network. Its widespread availability in the USA emphasizes its importance in the healthcare sector, providing essential support in combating bacterial infections.
Unveiling the Key Features of Augmentin
Augmentin's defining characteristics lie in its dual active ingredients, amoxicillin and clavulanate, which work together to enhance its antibacterial efficacy. This combination not only extends its antibacterial coverage but also minimizes the development of resistance, a significant advantage over monotherapy antibiotics. Its versatility in treating various infections makes it a staple in antibiotic therapy.
The drug's role in combating bacterial infections is supported by its ability to disrupt the bacterial cell wall synthesis, a vital process for bacterial growth and multiplication. This mechanism of action ensures effective eradication of the infection, showcasing Augmentin's strength as a therapeutic agent. Its broad-spectrum activity encompasses a wide range of bacteria, offering a comprehensive approach to infection management.
The Role of Amoxicillin and Clavulanate in Augmentin
Amoxicillin acts by inhibiting the bacterial cell wall synthesis, while clavulanate potassium blocks the enzyme beta-lactamase that some bacteria produce to resist antibiotics. This combination ensures Augmentin's effectiveness against beta-lactamase producing bacteria, expanding its utility in treating infections.
How Augmentin Combats Bacterial Infections
Augmentin's dual-action formula is designed to combat bacterial infections by targeting the bacteria's ability to build protective cell walls, leading to their destruction. This strategic approach allows Augmentin to treat a variety of infections, from common to more resistant strains, by ensuring the bacteria cannot survive or multiply.
The Mechanism of Action
Augmentin inhibits the synthesis of bacterial cell walls by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, leading to cell lysis and death. Clavulanate potassium extends this action by inhibiting beta-lactamases, enzymes that could otherwise render bacteria resistant to amoxicillin.
The Spectrum of Bacteria Affected
The antibiotic is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, E. coli, and Haemophilus influenzae, highlighting its broad-spectrum capability and making it a versatile choice for treating various infections.
The Effective Uses of Augmentin
Augmentin's effectiveness spans across a multitude of bacterial infections, making it a versatile tool in the arsenal against bacterial diseases. Its application ranges from respiratory tract infections to urinary tract infections, skin infections, and sinusitis, demonstrating its broad utility in clinical practice. The drug's ability to act against both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria ensures comprehensive coverage, addressing a wide spectrum of infectious agents.
Moreover, Augmentin serves as a preventive measure in certain medical procedures, helping to avoid potential bacterial infections. Its role in dental and surgical procedures as a prophylactic treatment showcases its importance in both therapeutic and preventive healthcare settings, underlining the drug's multifaceted utility.
Augmentin in Treating a Range of Infections
Augmentin is employed to treat various infections, including but not limited to, respiratory, urinary tract, skin, and sinus infections. Its broad-spectrum efficacy ensures it can effectively manage both acute and chronic conditions, providing a reliable solution for healthcare providers.
Augmentin as a Preventive Measure
In addition to its therapeutic uses, Augmentin is also used prophylactically in dental and surgical procedures to prevent infection, highlighting its role in safeguarding patients from potential bacterial threats during and after medical interventions.
Usage in Dental Procedures
Augmentin is prescribed to prevent bacterial infections during dental procedures, especially in patients at risk of endocarditis, ensuring a safer clinical outcome.
Recommended Dosages and Administration of Augmentin
The appropriate dosage of Augmentin varies depending on the severity and type of infection, as well as the patient's age and renal function. It is crucial for healthcare providers to adhere to recommended dosages to maximize efficacy while minimizing the risk of side effects. The flexibility in dosing forms, including tablets and suspensions, allows for tailored treatment plans to meet individual patient needs.
Administering Augmentin correctly is essential for achieving the desired therapeutic outcome. It is typically taken at the start of a meal to enhance absorption and reduce the potential for gastrointestinal upset. Patients are advised to complete the full course of therapy, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated and to prevent the development of resistance.
Dosage Considerations for Different Age Groups
Augmentin's dosage is adjusted based on age, weight, and kidney function, with specific guidelines provided for children and adults. This ensures effective and safe treatment across all age groups, taking into account the varying pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties in different populations.
Guidance on Augmentin Administration
For optimal absorption, Augmentin should be taken at the beginning of a meal. This strategy helps mitigate potential gastrointestinal side effects and maximizes drug efficacy. Proper hydration is also recommended to enhance absorption and support renal function during treatment.
A Comparative Look at Augmentin and Other Antibiotics
When comparing Augmentin to other antibiotics, particularly other beta-lactam antibiotics, its advantage lies in the inclusion of clavulanate potassium, which broadens its antibacterial spectrum by overcoming resistance mechanisms. This makes Augmentin particularly useful in treating infections caused by bacteria that produce beta-lactamase, a common resistance mechanism against penicillins and some cephalosporins.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of Augmentin relative to other antibiotics is crucial for healthcare providers when making treatment decisions. While Augmentin offers broad-spectrum coverage and the ability to combat beta-lactamase producing bacteria, it is important to consider potential side effects, the risk of antibiotic resistance, and specific patient factors when choosing the most appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Augmentin vs. Other Beta-lactam Antibiotics
Compared to other beta-lactam antibiotics, Augmentin's inclusion of clavulanate potassium allows it to effectively target a wider range of bacteria, including those resistant to other beta-lactams. This unique feature positions Augmentin as a preferred option for infections where resistance is a concern.
Understanding the Strengths and Limitations
While Augmentin is highly effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria, it is not suitable for all types of infections. Understanding its pharmacological profile, including its strengths in overcoming certain resistance mechanisms and its limitations, such as potential side effects and interactions with other medications, is essential for its optimal use in clinical practice.
FAQs Augmentin
What is Augmentin?
Augmentin is a brand-name prescription medication that contains a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. It is used to treat various bacterial infections.
How does Augmentin work?
Augmentin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. Amoxicillin, one of the active ingredients in Augmentin, kills bacteria by interfering with their cell wall synthesis. Clavulanic acid helps amoxicillin to be more effective against certain bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics.
What conditions does Augmentin treat?
Augmentin is commonly prescribed to treat infections such as sinusitis, pneumonia, ear infections, bronchitis, urinary tract infections, and skin infections caused by certain bacteria.
How should I take Augmentin?
Augmentin should be taken exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. It is typically taken orally, with or without food. Be sure to finish the entire course of medication even if you start to feel better, unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
What are the possible side effects of Augmentin?
Common side effects of Augmentin may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, headache, and skin rash. If you experience severe side effects such as severe diarrhea, difficulty breathing, or a skin rash with blistering, seek medical attention immediately.
Can I drink alcohol while taking Augmentin?
It is generally not recommended to drink alcohol while taking Augmentin. Alcohol may increase the risk of certain side effects such as stomach upset or liver damage.
Is Augmentin safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before taking Augmentin. They can weigh the potential risks and benefits of the medication for you and your baby.